The moment of truth – when sperm meets egg. It’s a process that has fascinated humans for centuries, yet remains shrouded in mystery. Fertilization is the crucial first step in creating life, and understanding how it works can be a game-changer for those struggling to conceive. From ovulation and sperm production to assisted reproductive technologies like IVF, there are many factors at play. But what exactly happens during fertilization? How do these two tiny cells come together in perfect harmony? In this detailed guide, we’ll take you through the entire process, from start to finish, addressing common challenges along the way. By the end of it, you’ll have a deeper understanding of how sperm meets egg and be better equipped to navigate the world of fertility.
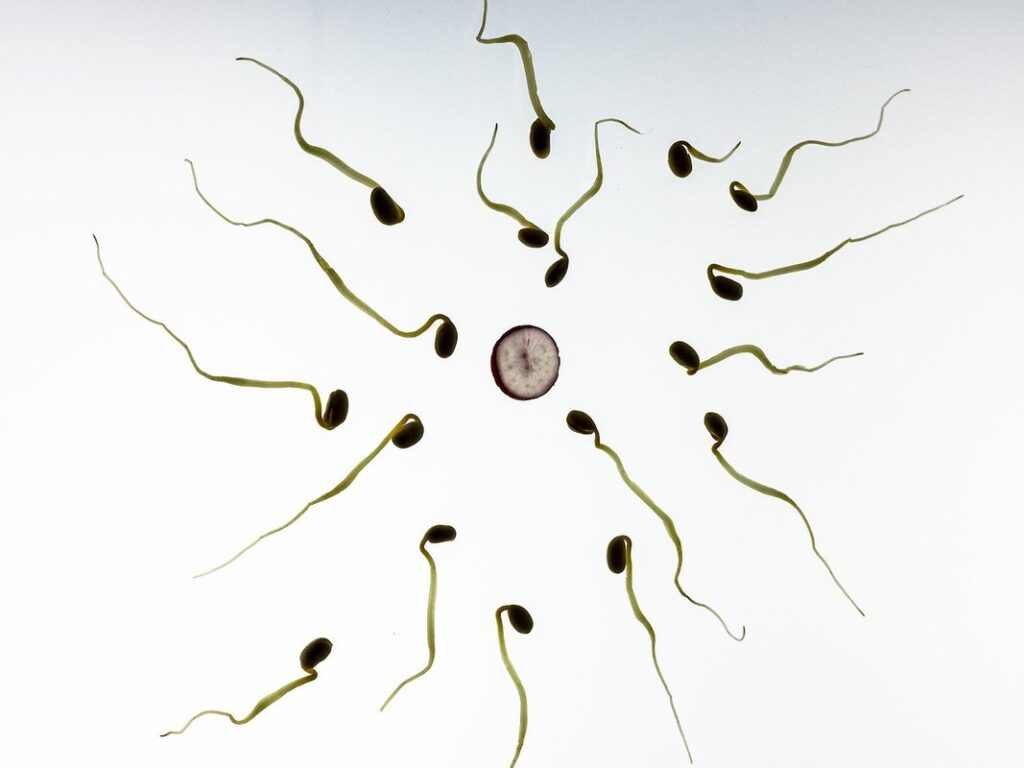
Understanding Human Reproduction
Let’s dive into the fascinating process of fertilization, where a single sperm meets an egg to form the foundation of a new life. This crucial moment sets the stage for embryonic development and growth.
Introduction to Ovulation and Menstruation
Understanding the intricacies of human reproduction is essential to grasping the fertilization process. Let’s dive into the basics of ovulation and menstruation.
The menstrual cycle is a complex process that involves the coordination of multiple hormones, including estrogen and progesterone. It typically lasts around 28 days, but can vary in length from woman to woman. The cycle begins on day one of menstruation, when the uterus sheds its lining in preparation for a new egg release.
During this time, the pituitary gland releases follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which stimulates the growth and maturation of follicles in the ovaries. As these follicles mature, they produce estrogen, causing the uterine lining to thicken in anticipation of implantation.
Ovulation typically occurs around day 14 of a 28-day cycle, when the dominant follicle releases an egg from the ovary into the fallopian tube. The released egg is then available for fertilization over the next 24 hours. After ovulation, progesterone levels surge to prepare the uterus for potential implantation.
Understanding these basic concepts provides context for the fertilization process and is crucial for anyone seeking to learn about human reproduction.
Hormonal Regulation of Fertilization
When it comes to fertilization, hormones play a crucial role in preparing the uterus for implantation. Two key players are estrogen and progesterone. Estrogen, produced by the ovaries, helps thicken the uterine lining, creating an optimal environment for a fertilized egg to attach. This process is often referred to as endometrial preparation.
Progesterone, also secreted by the ovaries, takes over once ovulation occurs. It maintains the thickened uterine lining and ensures it remains receptive to implantation. Together, these hormones create an ideal setting for a fertilized egg to settle and develop into a fetus. In the days leading up to ovulation, estrogen levels surge, causing the uterine lining to thicken. Once progesterone takes over, it supports continued growth and differentiation of the embryo.
Understanding this hormonal interplay is essential for anyone trying to conceive. Practically speaking, maintaining a healthy balance of these hormones through regular exercise, balanced diet, and stress management can support fertility. For instance, research suggests that regular physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which often disrupts hormone production.
The Journey of Sperm
As we follow the sperm on its incredible journey, you’ll learn how these tiny cells navigate the female reproductive system to reach the egg. From production to fertilization, it’s a fascinating process.
Sperm Production and Maturation
Sperm production is a complex and highly regulated process that occurs in the male reproductive system. It begins with spermatogenesis, which is the development of immature cells called spermatogonia into mature sperm cells. This process takes place in the seminiferous tubules of the testes, where the sperm cells undergo several stages of maturation.
During spermatogenesis, the spermatogonia multiply and differentiate into spermatocytes, which then undergo two cell divisions to produce spermatids. The spermatids mature further to become spermatozoa, also known as mature sperm cells. This entire process takes about 64-72 days and is influenced by various factors such as genetics, nutrition, and overall health.
A healthy diet rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and zinc can support optimal sperm production. For example, foods high in vitamin C like citrus fruits and leafy greens can help protect against oxidative stress that can damage sperm cells. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and getting enough sleep can also contribute to better sperm quality.
Factors such as age, smoking, and exposure to environmental toxins can negatively impact sperm production and quality. Therefore, it’s essential for men to adopt lifestyle habits that promote optimal reproductive health. By understanding the factors that influence sperm production, men can take proactive steps to improve their fertility and increase their chances of conceiving a healthy child.
Semen Analysis: What Your Results Mean
A semen analysis is a crucial test that helps assess male fertility and identify potential issues. It’s usually recommended for couples experiencing difficulty conceiving, but it can also be done as a routine check-up for men who are planning to start a family.
The typical report from a semen analysis includes several key parameters: sperm count, motility, morphology, and volume. Sperm count refers to the total number of sperm in one ejaculation, with a normal range typically being 15 million or more per milliliter. Motility measures how well the sperm can move, while morphology assesses the shape and structure of the sperm.
Common issues that may arise from semen analysis include low sperm count (oligospermia), poor motility (asthenozoospermia), or abnormal morphology (teratozoospermia). These conditions can be caused by various factors such as age, lifestyle choices (e.g., smoking, excessive heat exposure), and underlying medical conditions. If you’re concerned about your semen analysis results, consult a fertility specialist for personalized guidance on next steps. They may recommend further testing or treatment to address any underlying issues.
The Fertilization Process Itself
Let’s dive into the fascinating world of fertilization, where a single sperm meets an egg and changes everything. This is what happens during those few magical moments when life begins to take shape.
Sperm Capacitation: The Key to Fertilization
Sperm capacitation is a critical process that enables sperm to fertilize an egg. It’s a series of chemical changes that occur within the sperm itself, allowing it to bind to the outer layer of the egg and initiate fertilization.
When a sperm enters the reproductive tract, it undergoes a series of biochemical reactions that prepare it for fertilization. This includes the release of enzymes that break down the outer layers of the sperm, making it more motile and receptive to binding with the egg. As a result, the sperm’s membrane becomes more fluid, allowing it to penetrate the outer layer of the egg.
The capacitation process typically takes around 30 minutes to an hour, but this can vary depending on individual circumstances. During this time, the sperm undergoes significant changes in its plasma membrane and internal structure. This enables it to bind with the zona pellucida, a glycoprotein layer surrounding the egg that plays a crucial role in selecting which sperm will fertilize the egg.
The capacitation process is essential for successful fertilization, as an uncapacitated sperm will not be able to penetrate the outer layers of the egg. By understanding this critical step in the fertilization process, individuals can better appreciate the complex dance between sperm and egg that leads to conception.
Penetration and Fusion: How Sperm Meet Egg
The moment of fertilization is a remarkable process that marks the beginning of a new life. As we discussed earlier, for fertilization to occur, a sperm must first navigate through the outer layers of the egg. This journey is not an easy one, and only a select few sperm will make it past the egg’s defenses.
The outer layer of the egg, known as the zona pellucida, acts as a protective barrier that prevents multiple sperm from fertilizing the egg at once. However, this same layer also provides a path for a single sperm to penetrate. The sperm’s acrosome, a specialized cap on its head, contains enzymes that help break down the zona pellucida and allow the sperm to pass through.
As the sperm enters the egg, it fuses with the egg’s cell membrane, resulting in fertilization. This fusion is made possible by the presence of specific receptors on both the sperm and the egg, which guide them towards each other. Once fused, the sperm’s genetic material combines with that of the egg, creating a zygote – the first stage of a developing embryo.
Factors Affecting Fertilization Success
When it comes to fertilization, many things can impact its success. Let’s take a closer look at some of the key factors that can influence whether your embryo implants successfully.
Age and Fertility: How These Two Factors Interact
As we explore the factors that affect fertilization success, it’s essential to examine the relationship between age and fertility. Age is a significant factor that impacts both men’s and women’s reproductive health, influencing their ability to conceive.
For women, age affects fertility significantly. A woman’s egg supply declines with each menstrual cycle, but this decline accelerates after 35 years old. According to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM), the chances of getting pregnant decrease by 3-4% every year after 30. By 40, a woman’s chance of getting pregnant is around 10%. This decline in fertility is due to the gradual reduction in egg quality and quantity.
Men’s age also plays a crucial role in fertilization success. While men can father children at an advanced age, their ability to do so decreases with each year. Research suggests that a man’s sperm count and motility decrease significantly after 40 years old. However, this decline is gradual and may not be noticeable until much later.
When considering the interaction between age and fertility, it’s essential for couples to be aware of these age-related factors. If you’re planning to conceive or experiencing difficulty getting pregnant, consult with a healthcare provider about your specific situation and options available.
Lifestyle Choices That Impact Fertility
When it comes to fertilization success, lifestyle choices play a significant role. Your diet, exercise habits, stress levels, and exposure to environmental toxins can all impact the quality of your eggs and sperm.
A healthy diet rich in whole foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides essential nutrients for reproductive health. Foods high in antioxidants, such as berries, leafy greens, and nuts, help protect against oxidative stress that can damage egg or sperm cells. On the other hand, a diet high in processed meats, sugar, and saturated fats can lead to inflammation and reduced fertility.
Regular exercise also promotes healthy reproductive function by improving insulin sensitivity, regulating hormones, and reducing stress levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per day, such as brisk walking or cycling. Stress management techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can also help mitigate the negative effects of chronic stress on fertility.
Exposure to environmental toxins, such as pesticides, heavy metals, and plastics, has been linked to reduced fertility in both men and women. Limit your exposure by choosing organic produce when possible, avoiding plastic containers and water bottles, and using a water filter at home.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
Let’s explore some of the most effective assisted reproductive technologies that can help you conceive, such as IVF and ICSI. These techniques can boost your chances of getting pregnant.
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): The Basics
If you’re considering In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) as an option for building your family, understanding the basics of this process can help alleviate some of the anxiety and uncertainty that often accompanies it. At its core, IVF is a lab-based procedure where an egg is fertilized with sperm outside the body.
Here’s how it typically works: a woman undergoes hormone stimulation to produce multiple eggs, which are then retrieved through a minor surgical procedure. The eggs are mixed with sperm in a specialized culture medium and left to incubate for several days before being monitored for signs of fertilization.
Success rates for IVF vary depending on age, overall health, and other factors, but the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) reports that approximately 40-50% of cycles result in a live birth. While it’s a significant investment of time and emotional energy, many couples find the journey to be a transformative one.
Some things to keep in mind as you navigate the IVF process: be prepared for multiple attempts before achieving success, and don’t hesitate to reach out to your medical team with questions or concerns throughout the process. Researching support groups and online resources can also provide valuable guidance and reassurance.
Other ART Options: ICSI, IUI, and More
If you’re considering ART but haven’t found the right fit yet, don’t worry – there are other options available to help you achieve your goal. One of these alternatives is intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), a technique used in conjunction with IVF that involves injecting a single sperm directly into an egg.
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is another option, where sperm is inserted directly into the uterus during ovulation, increasing the chances of fertilization. Both ICSI and IUI are often recommended for couples facing specific fertility challenges, such as low sperm count or mobility issues.
Another valuable option to explore is embryo freezing, which allows you to freeze embryos created through IVF for future use. This can be especially useful if you’re not yet ready to start a family but still want to preserve your reproductive potential.
It’s essential to discuss these alternatives with your fertility specialist to determine the best course of action for your unique situation. By exploring different ART options, you’ll find what works best for you and increase your chances of success.
Addressing Fertilization Challenges
Fertilization challenges can be frustrating, but understanding the common issues that arise during IVF can help you navigate the process with greater ease and confidence. Let’s address these concerns together.
Common Issues with Ovulation and Menstruation
Many women experience challenges with ovulation and menstruation that can affect their ability to conceive. One of the most common issues is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), a hormonal disorder that affects approximately 5-10% of women of childbearing age. Women with PCOS often have irregular periods, infertility, and an increased risk of miscarriage.
Endometriosis is another condition that can cause ovulation and menstruation issues. This chronic gynecological disorder occurs when tissue grows outside the uterus, leading to pain, inflammation, and scarring. Endometriosis affects approximately 10% of women of reproductive age, and it’s a common cause of infertility.
Women with PCOS or endometriosis often experience difficulty getting pregnant due to ovulation problems. However, there are steps you can take to improve your chances of conceiving:
* Maintain a healthy weight through diet and exercise
* Manage stress levels through relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation
* Consider fertility medications to stimulate ovulation
* Work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan
By understanding the causes and symptoms of PCOS and endometriosis, women can take proactive steps towards addressing their unique challenges and improving their chances of getting pregnant.
What to Do When Fertilization Doesn’t Happen
If fertilization doesn’t happen, it can be a stressful and emotional experience for couples trying to conceive. First and foremost, it’s essential to recognize that difficulty conceiving is common and affects many people. However, if you’ve been trying for over a year without success, or if you’re under 35 with no regular menstrual cycles, it’s time to seek medical attention.
Your healthcare provider will likely recommend a series of tests to determine the cause of your fertility issues. These may include ovulation testing, semen analysis, and ultrasounds to examine your reproductive organs. If you’re over 35, your doctor may also order blood work to check for any underlying health conditions that could be affecting your fertility.
When it comes to testing options, don’t be afraid to ask questions or seek a second opinion. Some tests, like hysterosalpingography (HSG), can help identify blockages in the fallopian tubes, while others, such as laparoscopy, may be used to diagnose endometriosis or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). By working closely with your healthcare provider and being proactive about testing, you’ll be better equipped to navigate any challenges that come your way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the chances of success with IVF?
While IVF is a highly effective treatment for infertility, its success rates vary depending on several factors such as age, fertility issues, and quality of eggs and sperm. Generally, IVF success rates range from 40% to 70%, but it’s essential to discuss your individual situation with a fertility specialist.
How can I optimize my lifestyle choices to improve fertilization chances?
Maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, reducing stress levels, and limiting exposure to environmental toxins are all beneficial for improving fertilization outcomes. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins also supports overall reproductive health.
What are some common reasons why fertilization may not happen naturally?
Common issues with ovulation and menstruation, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, or unexplained infertility, can make it difficult to conceive naturally. Age-related fertility decline is another factor that can affect fertilization success.
Can I still have a successful IVF cycle if I’m over 40?
While age affects fertility, many women over 40 have successfully undergone IVF and conceived using their own eggs or those of an egg donor. However, it’s crucial to discuss your individual situation with a fertility specialist to determine the best course of action.
How soon can I try again after an unsuccessful fertilization attempt?
The decision on when to try again after an unsuccessful fertilization attempt depends on several factors, including the underlying cause of infertility and any treatment options explored. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider or fertility specialist for personalized guidance.
